Hyperpigmentation \ brown spots
What causes brown spots, and how can i get rid of them?
Brown spots, or hyperpigmentation, occur when the skin produces excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This can result from various factors like sun exposure, hormones, inflammation, and skin trauma. The most common types of hyperpigmentation include:
- Melasma: Splotchy, pigmented areas often on the face, commonly triggered by pregnancy or hormonal changes.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark patches left after skin trauma like pimples, burns, or scratches.
- Solar Lentigines/Freckles (Sun Spots/Age Spots): Brown or black spots, typically from prolonged sun exposure.
- Actinic Keratosis: Precancerous lesions caused by sun damage, appearing as rough, dry patches.
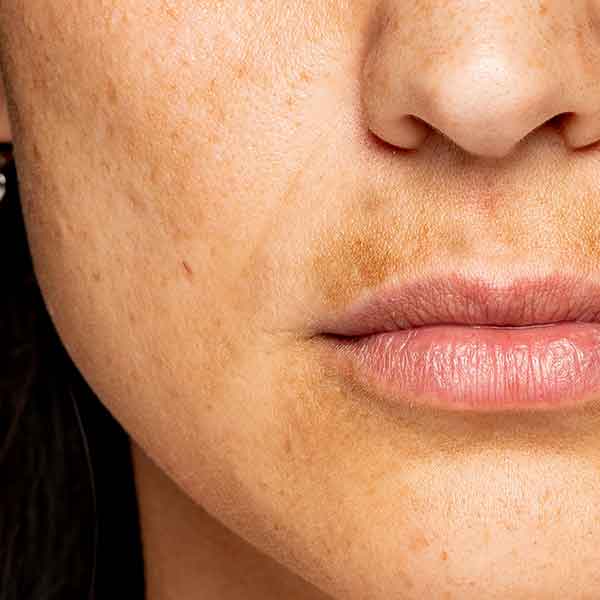
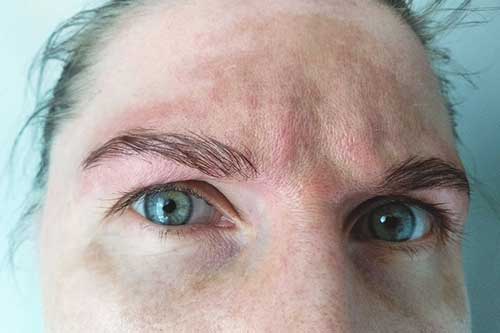
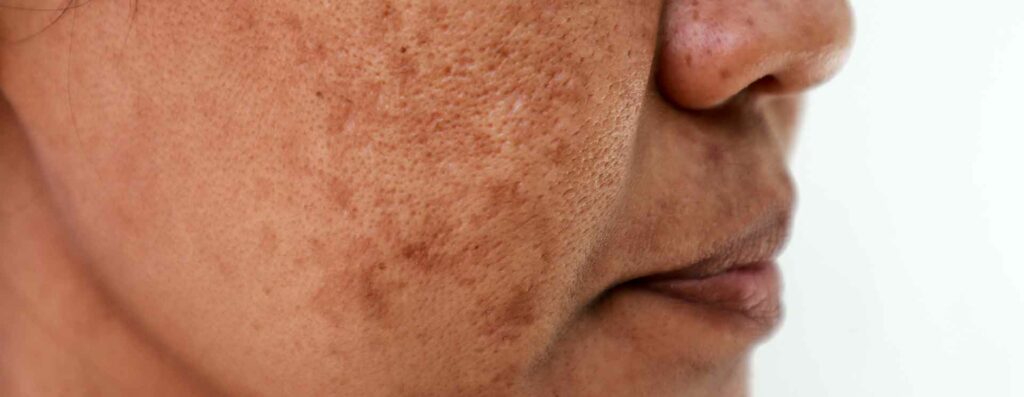
what causes hyperpigmentation?
Besides sun exposure, several other factors can cause hyperpigmentation, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy (melasma) or the use of birth control can lead to dark spots, especially on the face.
- Inflammation or Skin Injury: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs after skin trauma, such as acne, burns, cuts, or other skin irritations.
- Medications: Some drugs, like certain antibiotics, birth control pills, or chemotherapy treatments, can increase sensitivity to sunlight, leading to pigmentation changes.
- Age: As we get older, the skin’s ability to regenerate and repair itself decreases, leading to the appearance of age spots or liver spots, often from years of accumulated damage.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to develop certain types of hyperpigmentation, such as freckles or melasma.
- Chemical Exposure: Certain chemicals, like those found in fragrances or skincare products, can trigger pigmentation, especially if your skin reacts to them.
- Health Conditions: Disorders like Addison’s disease or certain types of anemia can cause increased pigmentation in the skin.
- Dietary Factors: Poor diet, nutrient deficiencies, or inflammation due to food sensitivities can also contribute to skin discoloration.
Each of these factors can stimulate the overproduction of melanin, leading to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
hyperpigmentation treatment options
- Chemical Peels: Target discoloration using acids like glycolic or salicylic.
- Microneedling Peels: A procedure where tiny needles create micro-injuries in the skin to stimulate collagen, reduce pigment and enhance the effectiveness of topical solutions such as a chemical peel to reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Non-Ablative Lasers like Clear + Brilliant is a non-invasive non-ablative laser that targets pigment and promotes skin rejuvenation without damaging the surface, helping to reduce dark spots and improve skin tone.
- Topical Treatments: Products with alpha/beta hydroxy acids, Vitamin C, and melanin suppressants (e.g., hydroquinone alternatives) can reduce dark spots.
- Melanin Suppressants: Help control melanin production to balance pigmentation.
The most commonly used drug for treating melasma is hydroquinone. It works as a skin lightening agent by inhibiting melanin production, which helps reduce dark spots. However, long-term use of hydroquinone can have potential side effects, so it’s important to use it under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Other options include:
- Tretinoin (Retinoid): Helps accelerate skin turnover, shedding dark skin cells and promoting clearer skin.
- Corticosteroids: In combination with other treatments, these can help reduce inflammation that may contribute to melasma.
- Tranexamic Acid: Can be used topically or orally to help reduce pigmentation, particularly in stubborn cases of melasma. It does not help with freckles and actinic keratosis.
These treatments are often used together for better results and should be combined with sunscreen to prevent further darkening. It’s important to choose treatments suited to your skin type to avoid worsening pigmentation, especially for darker skin tones.
Hyperpigmentation in Darker skin tones
Hyperpigmentation affects people of all skin tones, but it can appear differently in darker-skinned individuals compared to lighter-skinned individuals. Here are the key differences:
Visibility:
- Darker Skin: Hyperpigmentation is more noticeable due to higher melanin levels.
- Lighter Skin: Hyperpigmentation often appears as pink or red spots and is less intense.
Types of Hyperpigmentation:
- Darker Skin: More prone to Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) and melasma.
- Lighter Skin: Sun spots and redness are more common.
Risk of Scarring:
- Darker Skin: Higher chance of keloid scars and darkening after skin trauma.
- Lighter Skin: More likely to develop lighter or hypopigmented scars.
Treatment Sensitivity:
- Darker Skin: Needs gentler treatments to avoid worsening pigmentation.
- Lighter Skin: More tolerant but still at risk for irritation or temporary darkening with aggressive treatments.
Custom services for hyperpigmentation and brown spots
- New Client Consultation + Treatment
- Acne Deep Pore Cleansing Chemical Peel Facial + Light Therapy
- Back Facial + Light Therapy
- Body Chemical Peel
- Celebrity Skin Medium Depth Chemical Peel
- Men’s Facial + Light Therapy
- Microneedling Treatment
- Acne Facial For Teens + Light Therapy
- VI Peel
- The “Works” Chemical Peel Treatment
* All hyperpigmentation treatment protocols can and will be customized for your specific needs and skin tone
Everyone’s skin is different. The best thing is to do is book a New Client Consultation + Treatment to discuss and personalize your treatment with products to meet your individual needs.

